Employee motivation is a crucial factor that plays a significant role in the success of any organization. Motivated workers are more productive, engaged, and committed to their work, leading to a positive work environment and increased job satisfaction.
To achieve this, it is essential to understand the theories and benefits of a motivated workforce. Motivational theories explain what drives individuals to perform better, while the benefits of motivation at the workplace demonstrate its positive impact on both employees and the organization.
This article will explore the different theories and benefits of employee motivation, the advantages of a motivated workforce, and how to measure employee motivation in the workplace. So, why is motivation important for employees? Let’s find out.
What is employee motivation?

Employees’ motivation refers to the drive to perform their job responsibilities and achieve their career goals. Motivated employees are engaged, enthusiastic, and productive, resulting in higher job satisfaction, a better workplace atmosphere, and improved organizational performance.
To increase employee motivation and engagement, companies can implement various methods, such as providing feedback and open communication, expressing gratitude, encouraging a healthy lifestyle, providing opportunities for development, promoting organizational transparency and trust, and establishing achievable and quantifiable objectives. These methods create a positive work environment that fosters intrinsic motivation, improves productivity, and leads to better organizational results.
Employee motivation stats

The motivation of employees is crucial for maintaining a productive and engaged workforce. Research has shown that 55% of employees are unhappy and bored at work, which can lead to decreased productivity and increased absenteeism. On the other hand, happy employees experience 31% higher productivity and take 10 times fewer sick days. Motivated employees are more likely to feel a sense of identity from their job, report higher job satisfaction levels, and feel empowered to perform their best work.
Different motivational theories in the workplace, such as Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs and Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory, can increase motivation of employees in the workplace. Companies can also implement rewards and recognition programs, develop a strong company culture, and ensure employees feel respected and valued to motivate their workforce.
Wayes of measuring employee motivation statistics are important to determine the success of engagement strategies. Only 78% of companies have a documented employee engagement strategy, with less than half measuring success. Disengaged employees cost organizations between 550 billion annually. However, 80% of employees feel more engaged when their work motivations align with their organisation’s core values and mission.
Motivation for employee is important for maintaining a productive and engaged workforce. Companies can use different theories of motivation in business, such as rewards and recognition programs and a strong company culture. Measuring statistics about motivation is crucial to determining these strategies’ success and can result in significant benefits for the organization.
Types of employee motivation
Social motivation is a well-known sort of motivation. Employees that are socially driven get their energy from collaborating with others to achieve a common goal. They flourish in group settings because they like the sense of community and camaraderie it fosters. They become more engaged and committed when they feel that they are a part of something bigger than themselves.
The focus of monetary motivation, in contrast, is on cash rewards. Employee performance may be improved by rewarding them with wage increases, bonuses, or other financial incentives. While monetary incentive can have an immediate impact, it may be less successful over the long term because it ignores more fundamental underlying motivations.
Recognizing and appreciating employees’ efforts and successes is crucial, and recognition motivation is a key component of this. Organizations can reward their employees in a variety of ways, including with public acclaim, prizes, and unique privileges. Such acknowledgment and recognition boosts employees’ motivation and overall job satisfaction by cultivating a sense of worth and gratitude.
Giving workers more accountability and decision-making power inside their employment is a key component of responsibility motivation. Employees feel greater pride and ownership in their job when they are given larger, more important tasks to complete. As it offers a platform for growth and development, this kind of motivation is particularly helpful for people looking for professional progression prospects.
What are motivational theories?

Motivational theories delve into the intricate dynamics of human behaviour and the various motivation factors that drive individuals to engage in activities. Numerous motivational theories have emerged to shed light on these underlying mechanisms. These theories explore the interplay between the motivation to escape from aversive stimuli and the pursuit of rewarding experiences. Some theories focus on the satisfaction of physiological needs and the reduction of internal tension as driving forces. Others delve into the psychological discomfort that arises from conflicting beliefs or attitudes, motivating individuals to resolve this dissonance through behaviour change. Some theories propose a hierarchy of needs, ranging from basic survival requirements to higher-level aspirations.
A combination of conscious and unconscious factors can also influence motivation. For example, the desire to work may be driven by unconscious factors such as self-interest, while conscious factors could include a sense of duty towards family or societal expectations.
Furthermore, personality traits can shape an individual’s motivation. Traits like Machiavellianism, characterized by self-interest, desire for power, and narcissism, can influence one’s drive and behaviour. Some argue that high-powered individuals, such as CEOs and athletes, are likelier to exhibit Machiavellian qualities. However, it is also plausible that such positions foster the development of these traits as the pursuit and exercise of power may intensify the desire for even more power.
By comprehending the multifaceted nature of motivation and exploring various theories, individuals and organizations can gain valuable insights into human behaviour. This understanding empowers them to cultivate motivation effectively and leverage its transformative potential.
Motivational theories examples

Motivated employees tend to exhibit higher levels of engagement, satisfaction, and commitment towards their work, contributing to improved business outcomes. Many workplace motivation theories have been proposed over the years, each offering insight into what motivate employees at workplace and drives human behaviour.
Maslow’s Theory
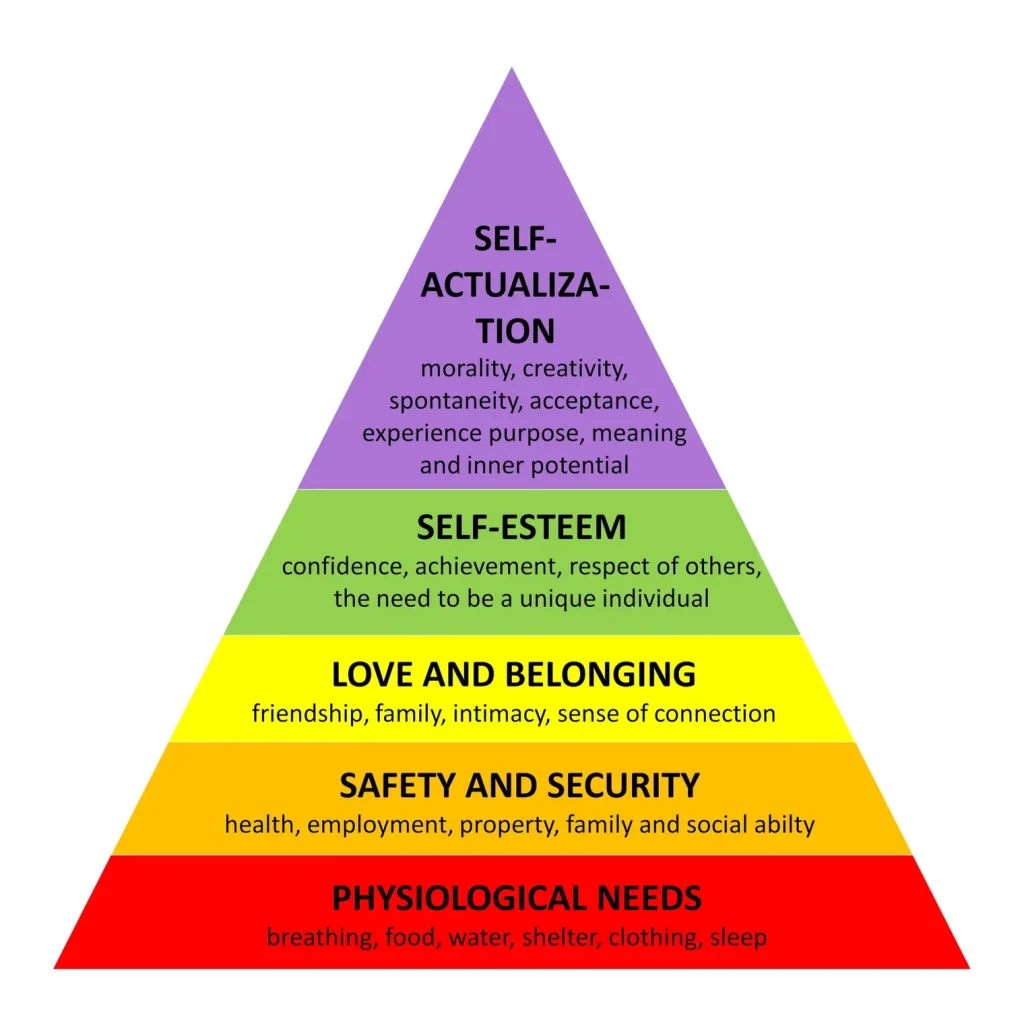
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs emphasizes that humans are motivated by a set of needs that are arranged in a pyramid of five levels. Each need is classified based on its importance and priority. Maslow stated that once a need is met, it loses its ability to motivate, and the next need in the hierarchy takes its place.
The five categories are physiological, safety, social/belongingness, self-esteem, and self-actualization. Physiological needs are the most basic needs, such as food, water, and sleep. Safety needs include comfort, security, and stability. Social needs encompass friendships and relationships, while self-esteem needs are the desire for a positive self-image, prestige, and status. Self-actualization needs are at the top of the pyramid and deal with the desire to grow, advance, and be creative.
HR professionals can use this theory to attract and retain talented employees by providing regular salaries, a safe working environment, retirement plans, job security, teamwork, rewards, and challenging work opportunities.
Nudge Theory
Nudge theory is a highly effective approach to workplace motivation and a central concept in behavioural economics. It has been developed by Cass Sunstein and Richard Thaler, who define it as any aspect of choice architecture that influences people’s behaviour predictably without removing any options or changing incentives.
This theory influences employees towards positive choices rather than forcing them to comply. For instance, employers can nudge employees to attend training programs and advance their careers, thereby increasing organisational productivity. The theory can also encourage employees to adopt healthy lifestyles by developing health plans and organizing sports competitions.
Two types of incentives are motivating employees in the workplace – intrinsic and extrinsic. Intrinsic motivation comes from within and arises from a deep-rooted desire to perform a task because it satisfies the employee. In contrast, extrinsic motivation is driven by external rewards such as money or non-monetary ones such as fame or position. Employers can use both intrinsic and extrinsic motivators to encourage their employees. They can use tangible rewards like pay raises and other benefits to motivate employees extrinsically, ultimately leading to intrinsic motivation.
McClelland’s Theory
McClelland’s Theory is a motivational theory that asserts that we all have three driving motivators that are not dependent on our gender or age. These three motivators are achievement, affiliation, and power, and one of them will be dominant in our behaviour, depending on our life experiences. According to McClelland, understanding these motivators is crucial in motivating others in the workplace.
Achievement is a motivating factor for people who must demonstrate competence and accomplish their goals. These people prefer tasks that allow them to take personal responsibility and provide results based on their efforts. Acknowledging their progress is also vital as they seek quick recognition for their achievements. Employees with high achievement motivation at workplace can be motivated by challenging projects that test their abilities and provide growth opportunities.
Affiliation is a driving motivator for those who need love, belonging, and social acceptance. People with high affiliation needs are motivated by being liked and accepted by others. They enjoy participating in social gatherings and building strong relationships. They may also be uncomfortable with conflict, preferring to maintain harmony in their relationships. Employees with high affiliation motivation can be motivated in the workplace by creating a friendly and supportive work environment that fosters positive colleague relationships.
Power is the third driving motivator in McClelland’s theory. People with high power motivation desire situations in which they can exercise power and influence over others. They aspire to positions with status and authority and are more concerned with their level of influence than with effective work performance. Employees with high power motivation can be motivated in the workplace by providing opportunities to take charge of tasks and lead projects.
Understanding McClelland’s Theory is essential to motivate staff in the workplace. By recognizing employees’ dominant motivators, employers can provide tasks, projects, and opportunities that align with their needs and desires.
Benefits of Highly Motivated Employees
Organizations can create a culture that fosters engagement, productivity, and growth by understanding the benefits of motivated employees for the organization. Let’s dive into the advantages of motivation in management and how it can impact the workplace.

Stronger Team Dynamics:
When employees are highly motivated, they tend to have a more positive impact on team dynamics. Their enthusiasm and engagement can lead to effective collaboration, clear communication, and a supportive culture. This, in turn, can boost team productivity, morale, and overall performance, benefiting both the team members and the organization.
Better Problem-Solving:
Motivated employees are often proactive when it comes to identifying and solving problems. They take ownership of issues and are unafraid to take risks or suggest new solutions. This can result in faster and more effective problem-solving, saving the organization time and resources. Additionally, satisfied employees can bring fresh perspectives and ideas, leading to more innovative and creative solutions.
Enhanced Reputation:
Employees who are highly motivated are more likely to be committed to the organization and its goals. They may go above and beyond their job responsibilities, resulting in positive word-of-mouth and improved customer satisfaction. This can enhance the organization’s reputation in the marketplace, attract new customers, and retain existing ones. A strong reputation can lead to increased revenue and growth opportunities for the organization.
Proactivity:

Motivated employees tend to be proactive in seeking opportunities for growth and improvement. They are self-reflective and always looking for ways to enhance their performance. They take the initiative and do not wait for feedback or direction from others. This proactive approach can increase efficiency, higher quality work, and a more engaged workforce.
Improved Health and Wellness:
Highly motivated employees often prioritize their physical and mental health. They understand the importance of maintaining good health and well-being, which can reduce absenteeism and healthcare costs for the organization. Additionally, organizations prioritising employee wellbeing often see higher levels of job satisfaction, retention, and productivity.
Innovation and Creativity:
Motivated employees are often more creative and innovative. They are willing to take risks and experiment with new ideas, and are not afraid to challenge the status quo. This can lead to developing new products, services, and processes that can help the organization stay competitive in the marketplace. Additionally, a culture of innovation can attract top talent and help to retain existing employees who value opportunities for growth and development.
Conclusion

Motivated employees exhibit higher productivity, engagement, and commitment towards their work. Different motivational theories, such as Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs and Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory, can increase leadership motivation in the workplace. Rewards and recognition programs, a strong company culture, and ensuring employees feel respected and valued are effective strategies to motivate the workforce.
Measuring employee motivation benefits through employee surveys, performance metrics, one-on-one meetings, absenteeism and turnover rates is crucial to determining engagement strategies’ success. Organizations can improve employee satisfaction by implementing effective engagement strategies and understanding motivational theories, leading to significant benefits for the organization.
FAQ
What is the importance of motivational theories for employees?
Motivational theories are important for employees because they provide valuable insights into what drives individuals to perform better in the workplace. These theories help organizations understand the underlying factors that influence employee motivation, allowing them to create strategies and initiatives that enhance employee engagement, satisfaction, and productivity. By applying motivational theories, organizations can tailor their approaches to meet the diverse needs and preferences of employees, ultimately fostering a positive work environment and promoting individual and organizational success.
Which theory of motivation is the best and why?
There is no single theory of motivation that can be considered the best as different theories have different strengths and applications. The effectiveness of a motivational theory depends on various factors, including the specific context, individual differences, and organizational goals.
What are the benefits of employee motivation for the organization?
Motivated employees benefit the organization in several ways. They are more productive, which leads to increased efficiency and higher-quality work. They are also more engaged and committed, resulting in lower turnover rates and higher retention of top talent. Furthermore, a motivated workforce fosters innovation, teamwork, and a positive work culture, ultimately contributing to the organization’s success.
What is Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs theory?
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs theory suggests that individuals are motivated by a series of needs that are arranged in a hierarchical order. These needs include physiological needs, safety needs, social needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization needs. As employees fulfill each need, they become motivated to pursue higher-level needs.


